1. The concept of HALT&HASS testing
HALT (Highly Accelerated Life Test) originally means: High Accelerated Life Test;
HASS (Highly Accelerated Stress Screen) originally means: high accelerated stress screening.
HALT&HASS is a test method for design quality verification and manufacturing quality verification extended by the US military, and has now become the standard product verification method in the US electronics industry.
It shortens the reliability testing of new products, which originally required 6 months or even 1 year, to one week, and the product problems discovered during this week are almost identical to those found in customer applications. Therefore, the HALT&HASS testing method has become a necessary validation for new products before they are launched.
2. Advantages of using high acceleration life testing
Adopting high acceleration life testing can shorten the product development cycle and reduce the product's guarantee cost:
Identify potential defects and design weaknesses in the product;
Evaluate and improve design margins;
Reduce the probability of on-site failure;
Adopting high acceleration life testing can reduce the mortality rate of products during production introduction:
Detect and correct design process changes;
Accelerate production quality and on-site reliability;
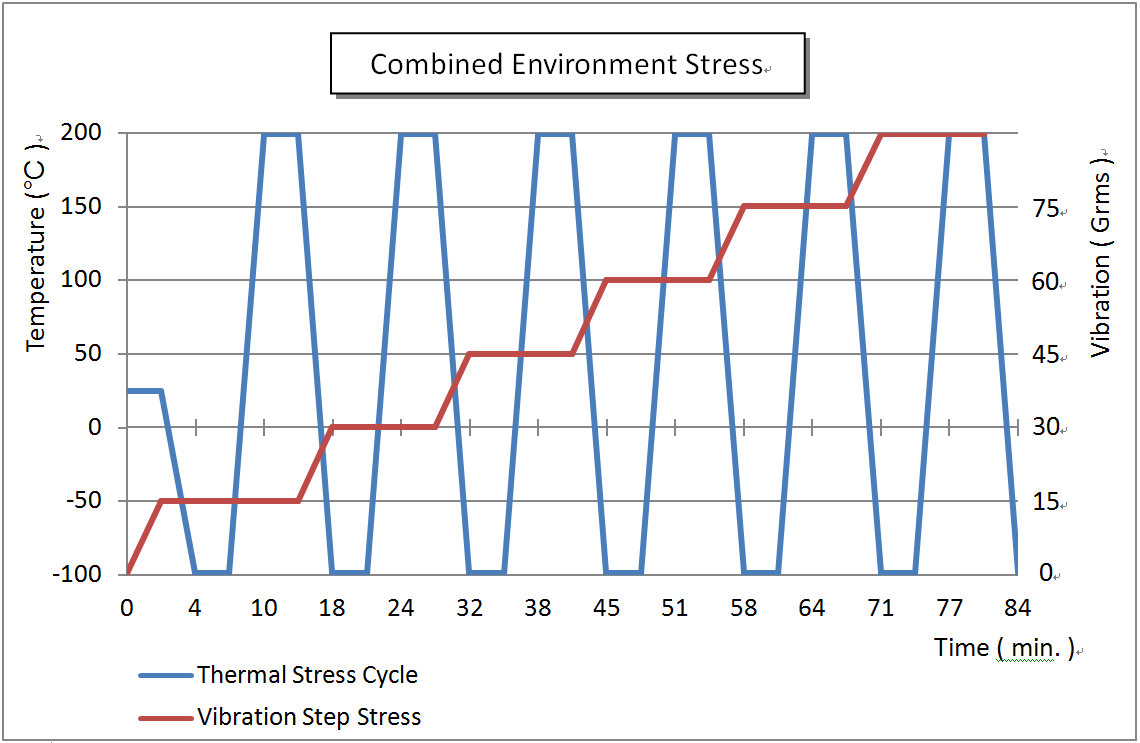
Typical comprehensive environmental stress test curve
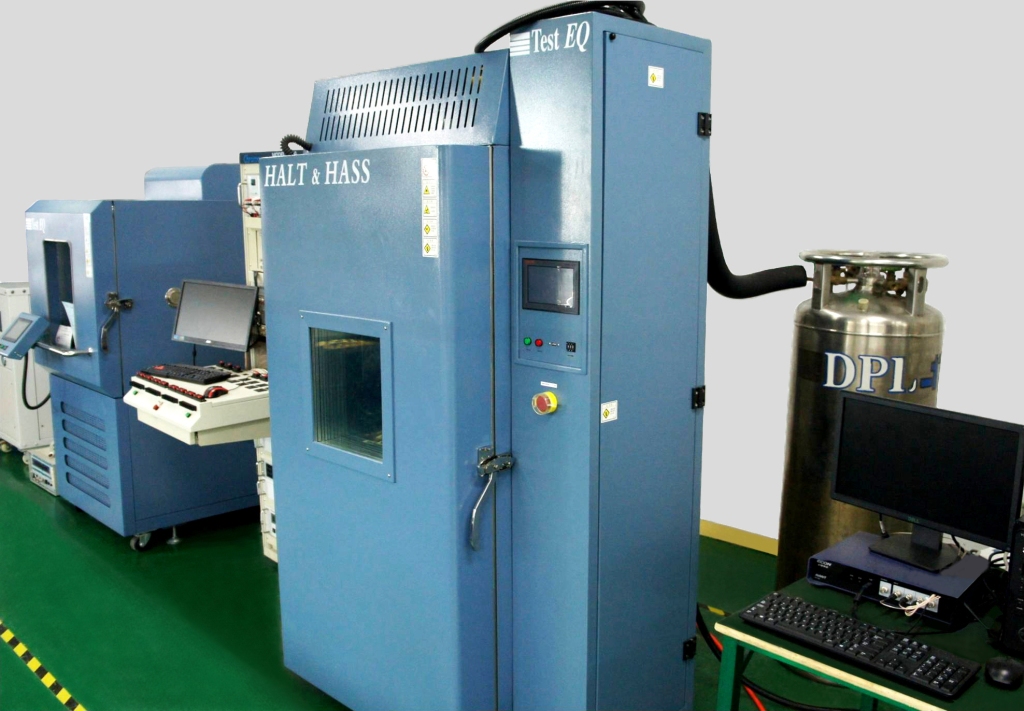

HALT&HASS testing system introduced by Yiguang Technology
3. HALT testing
HALT is an experimental method that discovers design flaws and potential weaknesses by subjecting the tested object to different stresses. The main purpose of HALT is to increase the limit value of the tested object, thereby enhancing its robustness and reliability. HALT is a method of applying step stress to products, which enables early detection of product defects, design margins, and structural strength limits. The stress applied to the product includes vibration, high and low temperature, temperature cycling, power switch cycling, voltage margin and frequency margin testing, etc. This test can quickly identify defects in product design and manufacturing, improve design defects, increase product reliability, and shorten its launch cycle. At the same time, it can also establish basic data for design capability, product reliability, and important basis for future research and development.
Simply put, HALT is a program consisting of continuous testing, analysis, validation, and correction, with the key being the analysis of the root causes of all faults.
The main testing functions of HALT are as follows
Utilize high environmental stress to stimulate product design defects and improve them;
Understand the design capability and failure modes of the product;
◆ As a reference for high stress screening and audit specification development;
Quickly identify defects in the product manufacturing process;
◆ Increase product reliability and reduce maintenance costs;
Establish a product design capability database to provide a basis for research and development and shorten the design and manufacturing cycle.
HALT is applied in the research and development stage of products, which can detect weak links in product reliability early. The applied stress is much higher than the stress of the product during normal transportation, storage, and use.
HALT is divided into four main trial processes
◆ Temperature stress;
◆ High speed temperature conduction;
◆ Random vibration;
Temperature and vibration combined with stress.
In the HALT test, the operable and destructive limits of the tested object under temperature and vibration stress can be found. The equipment used is the OVS Combined Stress System designed by QualMark, with a temperature range of -100 ℃ to+200 ℃, a maximum temperature change rate of 60 ℃/min, and a maximum acceleration of up to 60Grms. Additionally, the vibration machine and temperature chamber are designed to simultaneously apply temperature and vibration stress to the tested object. The general situations of the four trial processes are explained below:
(1) Temperature stress (HL high and low temperature test chamber)
This experiment is divided into two stages of stress: low temperature and high temperature. Firstly, perform the low-temperature stage stress, set the starting temperature to 20 ℃, cool down by 10 ℃ in each stage, and maintain the stage temperature stable for 10 minutes. Then, perform at least one functional test at the stage stable temperature. If everything is normal, lower the temperature by another 10 ℃ and maintain it for 10 minutes before executing the function. Repeat this process until a functional failure occurs to determine whether the operating limit or damage limit has been reached; After completing the low-temperature stress test, the high-temperature stress test can be performed according to the same procedure. That is, the comprehensive environmental stress testing machine starts from 20 ℃, heats up by 10 ℃ in each stage, and maintains the temperature stable for 10 minutes. Then, the functional test is performed until the high-temperature operating limit and high-temperature failure limit are found.
(2) High speed temperature conduction
This experiment will use the low and high temperature control limits obtained from the stress testing in the temperature stage as the high and low temperature limits here, and conduct 6 cycles of high and low temperature changes within this interval at a rapid temperature change rate of 60 ℃ per minute. At the highest and lowest temperatures of each cycle, stay for 10 minutes and stabilize the temperature before performing the functional test. Check whether the test object has a recoverable fault and find its operable limit. There is no need to search for the boundary of destruction in this experiment.
(3) Random vibration (Aisili vibration testing machine)
This experiment starts with a G value of 5g, increases it by 5g in each stage, and performs a functional test under continuous vibration conditions after maintaining it for 10 minutes in each stage to determine whether it has reached the operable or destructive limit.
(4) Temperature and vibration combined stress (ASLI temperature humidity vibration three comprehensive testing machine)
This experiment combines high-speed temperature conduction and random vibration testing to make the accelerated aging effect more significant. Here, the previous rapid temperature change cycle conditions and temperature change rate are used, and random vibration is started from 5g and gradually increased by 5g for each cycle. The highest and lowest temperatures of each cycle are maintained for 10 minutes. After the temperature stabilizes, functional testing is performed, and this process is repeated until the operable and destructive limits are reached.
Note: The above experimental parameters are only examples, and the specific product depends on the product requirements.
Record any abnormal states generated by the tested object in the above four test cycles, analyze whether these problems can be overcome by changing the design, and make modifications before proceeding to the next step of testing. By increasing the operational and destructive limits of the product, the goal of improving reliability can be achieved.
4. HASS testing
HASS is applied in the production phase of products to ensure that all improvement measures found in HALT are implemented. HASS can also ensure that no new defects are introduced due to changes in production processes and components.
HASS includes the following content
◆ Conduct pre screening to eliminate hidden defects that may develop into obvious defects;
◆ Conduct detection and screening to identify obvious defects;
◆ Fault analysis;
Improvement measures.
The purpose of applying HASS is to detect potential quality hazards in mass-produced products in a very short period of time. This experiment includes three main stages:
HASS Development (HASS Test Plan Phase)
◆ Proof of Screen (Plan Verification Phase)
Production HASS (HASS execution phase)
The testing process for general electronic products:
(1)HASS Development
The HASS test plan must refer to the results obtained from the previous HALT test. Generally, the operable limits of high and low temperatures in the combined stress of temperature and vibration are reduced by 20%, while the vibration condition is set as the initial condition for the HASS test plan at 50% of the failure limit G value. Then, based on these conditions, perform temperature and vibration combined stress tests, and observe whether there are any faults in the tested object. If a malfunction occurs, it is necessary to first determine whether it is caused by excessive environmental stress or the quality of the tested object itself. When it belongs to the former, the temperature and vibration stress should be relaxed by 10% before testing. When it belongs to the latter, it indicates that the current testing conditions are effective. If no faults occur, the testing environment must be subjected to an additional 10% stress before further testing.
(2)Proof-of-Screen
When establishing the HASS Profile, two principles should be noted: firstly, it must be able to detect potential hazards that may cause equipment failure; Secondly, after testing, it will not cause equipment damage or "internal injury". In order to ensure that the results obtained during the HASS test plan phase comply with the above two principles, it is necessary to prepare three test samples and make some defects on each sample that have not been manufactured or assembled according to standard processes, such as component floating, empty welding, and improper assembly. Test each test sample based on the conditions obtained during the HASS testing plan phase, and observe whether artificial defects on each sample can be detected to determine whether to tighten or relax the testing conditions, in order to achieve the expected results of the HASS Profile.
After completing the effectiveness test, the HASS Profile should be tested 30-50 times with new test samples and adjusted conditions. If no damage occurs due to improper stress, it can be determined that the HASS Profile has passed the plan validation phase test and can be used for Production HASS. On the contrary, further review and adjustment of testing conditions are necessary to obtain the best combination.
(3)Production HASS
Any HASS Profile that has been tested by Proof of Screen is considered a fast and effective quality screening tool, but it still needs to be adjusted appropriately in conjunction with any anomalies reported by customers after the product has been used. In addition, when there are design changes, the testing conditions are also modified accordingly.